JavaScript Async and Await

JavaScript Async and Await
JavaScript Async and Await make asynchronous JavaScript easier to read and write. They are built on top of Promises, but feel more like normal, synchronous code.
Why Async/Await?
Before async/await, we used:
-
Callbacks → callback hell 😵
-
Promises with
.then()→ better, but still nested sometimes
async/await solves this by making async code look clean and sequential ✅
1️⃣ The async Keyword
-
Used before a function
-
Always returns a Promise
-
If you return a value, JavaScript automatically wraps it in a Promise
2️⃣ The await Keyword
-
Used inside an async function only
-
Pauses execution until the Promise resolves
-
Makes async code behave like synchronous code
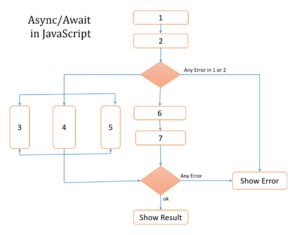
How Async/Await Works (Flow)
👉 JavaScript waits at await
👉 Other code can run
👉 Execution resumes when Promise resolves
3️⃣ Async/Await with fetch() (Real Example)
✔ No .then() chaining
✔ Clean & readable
4️⃣ Error Handling with try...catch
🔐 Errors are handled just like normal JavaScript
5️⃣ Multiple Await Calls (Sequential vs Parallel)
❌ Sequential (Slower)
✅ Parallel (Faster)
6️⃣ Async Arrow Function
Common Mistakes ❌
❌ Using await outside async
❌ Forgetting try...catch
❌ Assuming await blocks the whole program (it doesn’t!)
Quick Summary 📌
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
async |
Makes a function return a Promise |
await |
Waits for a Promise to resolve |
try...catch |
Handles async errors |
| Cleaner | Replaces .then() chains |