Introduction to DSA

Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA)
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) form the foundation of computer science.
They help us store data efficiently and solve problems optimally—a must-know topic for exams, interviews, and real-world software development.
1️⃣ What is Data?
Data is raw information such as:
-
Numbers (10, 25)
-
Text (“Swift”, “Apple”)
-
Records (student details)
To use data effectively, we need proper organization and processing methods.
2️⃣ What are Data Structures?
A Data Structure is a way of organizing, storing, and managing data so it can be used efficiently.
Examples
-
Array
-
Stack
-
Queue
-
Linked List
-
Tree
-
Graph
-
Hash Table
Choosing the right data structure improves performance and memory usage.
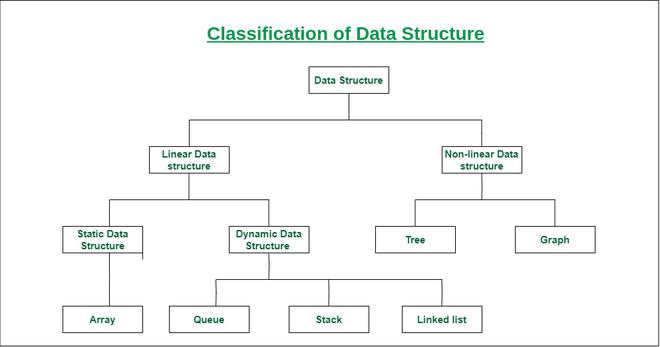
3️⃣ Types of Data Structures
1. Linear Data Structures
Data elements are stored sequentially.
-
Array
-
Linked List
-
Stack
-
Queue
Example: List of numbers
2. Non-Linear Data Structures
Data elements are stored hierarchically or graph-like.
-
Tree
-
Graph
Example: File system, social networks
4️⃣ What is an Algorithm?
An Algorithm is a step-by-step procedure to solve a problem.
Example (Algorithm to add two numbers)
-
Start
-
Take two numbers
-
Add them
-
Display result
-
End
Algorithms focus on logic and efficiency.
5️⃣ Characteristics of a Good Algorithm
✔ Clear and unambiguous
✔ Finite number of steps
✔ Efficient (time & space)
✔ Correct output for all valid inputs
6️⃣ Why Study DSA?
DSA helps you:
-
Write optimized code
-
Improve problem-solving skills
-
Crack coding interviews
-
Build scalable applications
Almost all product companies test DSA skills.
7️⃣ Time & Space Complexity (Basic Idea)
Time Complexity
Measures how fast an algorithm runs.
Examples:
-
O(1) → Constant time
-
O(n) → Linear time
-
O(log n) → Logarithmic time
Space Complexity
Measures extra memory used by an algorithm.
Efficient algorithms use less time and less space.
8️⃣ Data Structures vs Algorithms
| Data Structures | Algorithms |
|---|---|
| Store data | Process data |
| Example: Array | Example: Sorting |
| Focus on organization | Focus on logic |
| Memory-oriented | Time-oriented |
9️⃣ Real-Life Examples
-
Array → Marks of students
-
Stack → Undo/Redo in apps
-
Queue → Ticket booking system
-
Tree → Folder structure
-
Graph → Google Maps routes
🔟 DSA in Programming Languages
DSA concepts are language-independent and can be implemented in:
-
C / C++
-
Java
-
Python
-
Swift
-
JavaScript
Logic stays the same, syntax changes.
Common Interview Questions (Intro Level)
Q1. What is DSA?
👉 Study of data storage and problem-solving techniques
Q2. Why are data structures important?
👉 They improve efficiency
Q3. What is the difference between array and linked list?
👉 Memory layout & access method
Summary
✔ Data Structures organize data
✔ Algorithms process data
✔ DSA improves performance & scalability
✔ Essential for exams & interviews
✔ Core of software engineering