SciPy Getting Started

SciPy – Getting Started (Step-by-Step Guide)
This section will help you start using SciPy practically. We’ll cover installation, basic imports, first programs, and how SciPy works with NumPy.
Important: SciPy is built on NumPy, so NumPy must be installed first.
1. Prerequisites
Before SciPy, make sure you know:
-
Python basics
-
NumPy arrays & operations
Check NumPy:
2. Installing SciPy
Using pip (most common)
Using Anaconda
Verify Installation
If no error appears → SciPy installed successfully.
3. Importing SciPy
SciPy is modular, so you usually import only what you need.
Or import specific modules:
4. First SciPy Example (Linear Algebra)
SciPy extends NumPy’s math power.
Here:
-
NumPy creates the array
-
SciPy performs advanced matrix operations
5. Solving Linear Equations
Equation:
Code:
6. Optimization (Finding Minimum)
Find minimum of a function:
Used heavily in machine learning & engineering.
7. Integration (Area Under Curve)
Compute:
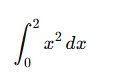
8. Basic Statistics with SciPy
Much more powerful than Python’s statistics module.
9. SciPy Workflow (Very Important Concept)
Typical SciPy workflow:
Example:
10. When to Use SciPy?
Use SciPy when you need:
-
Optimization
-
Integration / differentiation
-
Signal processing
-
Statistics & probability
-
Linear algebra (advanced)
-
Engineering simulations
For:
-
Tables & CSV → Pandas
-
Visualization → Matplotlib
-
ML Models → Scikit-learn
Common Beginner Mistakes
- Trying SciPy without NumPy
- Importing entire SciPy unnecessarily
- Using loops instead of vectorized operations
- Confusing SciPy with Pandas
Summary
- SciPy is an advanced scientific library
- Built on NumPy arrays
- Organized into powerful submodules
- Essential for data science, ML & engineering
- Faster and more accurate than manual math

